Find route path is an analyzing tool that helps you identify unoccupied fiber or thread paths in the network.
1.Select Tools > Find route path. The tool is displayed as a new tab in the side bar.
2.Select a Start object, press Select object and then select a node object in the map.
3.Select an End object, press Select object and then select a node object in the map.
It is possible to trace the selected objects in the map using the trace buttons to the left of the selected object. |
4.Press Search.
The tool presents possible paths along connected routes between the selected start and end objects. The 10 shortest paths are listed.
When you select one of the suggested route paths it is highlighted in the map.
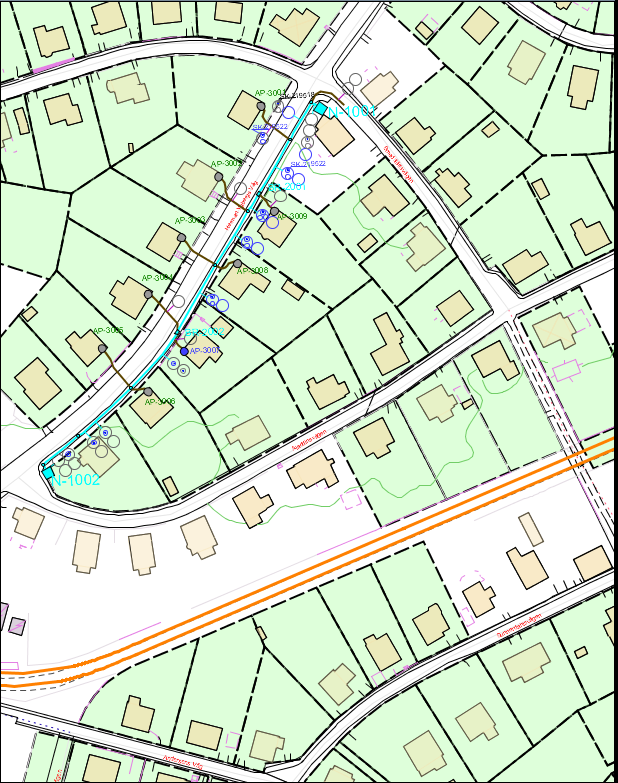
Double-click a folder to expand all steps along the route path.
In the expanded view unoccupied cables and pipes are reported, both combined for the entire route path, and for every route along the path.
Save the result from the Find route path function to saved object list: 1.In the result list, right click on the route path and select Add to saved object list. For more information about the saved object list, see Run queries on results within saved object list. |
More information
Show schematic map of cables and pipes along the route path
Right-click a route path folder and select Show cable paths or Show pipe paths. A diagram opens in a new window:
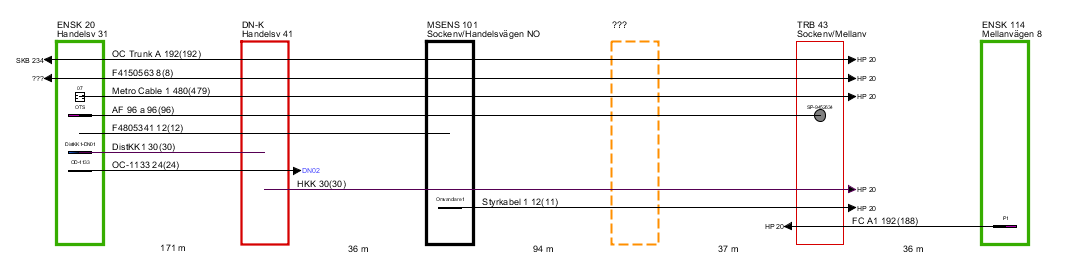
Press F5 to put out the highlighted diagram.
•The diagram displays all nodes that forms the selected route path, starting node to the left, end node to the right, and in between all intermediate nodes. Between the nodes the route length is shown.
•Cables running entirely or partially along the route path are displayed as lines, with a text label showing ID, number of fiber or threads, and - in parenthesis - number of unoccupied fibers/threads, i.e without a service or connection.
•If the cable is connected to any equipment in any of the nodes, this is also displayed. If the cable branches off, this is shown with an arrow symbol and the ID of the node that the cable is running towards (Note! This is not always the same node as the one the cable ends in).
•For Show pipe paths, pipes and ducts rather than cables are shown in the diagram. The layout is very similar to that of the cable but this diagram opens up a couple of interesting use cases.
oIf a cable is to be placed in a sequence of pipes/ducts in order to reach its intended destination, the find route path can be run with the intended start and end for the cable as start and end nodes. The show pipe path diagram can then be used as a guidance for finding the sequence of suitable pipes/ducts. By using the command Put cable/pipe in route/pipe the cable can be extended step by step along the path, using the available pipes and ducts.
oIf the Find route path is run with the start node at the start of a multiduct and the end at the end of that multiduct, the diagram shows a nice overview of the ducts in the multiducts, including the ducts as seen from the end node.