Note, To use the features of the GPS menu, a GPS device must be connected to the device.
Zoom to GPS position
To zoom to the current position, select GPS > Go to GPS position.
Track GPS-position
For the map to automatically follow GPS position, open the GPS menu and select the Track GPS menu and mark the check box.
Select GPS
In addition to what is described about automatic GPS device selection, you may still want to lock to a particular device. For example, if there is a good and a bad GPS device and the bad GPS get a position first (which may not be so accurate).
The Select GPS option shows the devices that dpSpatial managed to detect as GPS devices, all serial ports are not listed. The Select GPS dialog opens:
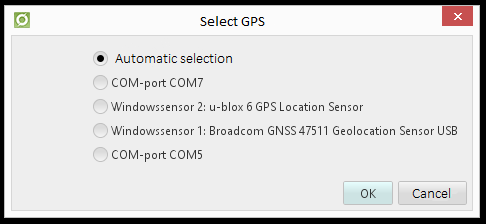
If no devices are found, the following dialog opens:
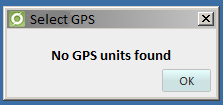
If any GPS devices have been found and any of these are selected, all positions will go over to use that device and that setting will be saved in the user settings. This means that at the next startup of dpSpatial, the GPS device is selected (if it is in the system with the exact name and numbering). If it is not, dpSpatial passes to automatic selection, just as if you choose it in the dialog.
A GPS device selected via auto-select (to get a position) is not saved as an option, although it appears as highlighted in the dialog. You can confirm this with OK. This has been selected because the normal function is that dpSpatial should select the device itself and the user does not have to do this locking of the GPS device. This would cause problems if the device renames, get another number in the COM # name (for example, associates a Bluetooth device).
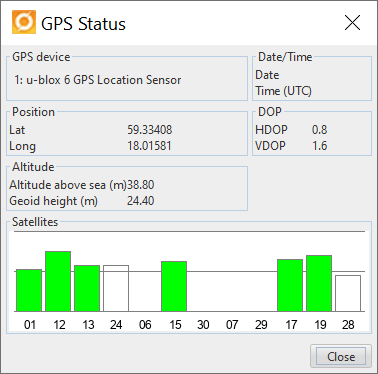
Read GPS status
To read date, time (UTC) and coordinates, select GPS > Show GPS status.
Import GPS-tracks
This feature is used to import positions in files that have been saved during flight inspections. The file has three columns; time, latitude and longitude that are tab-separated.
Examples of what the file might look like:
Time format example:
2008-04-01 11:20:31
Latitude format example:
59.033333232 (WGS84)
Longitude format example:
18.434534343 (WGS84)